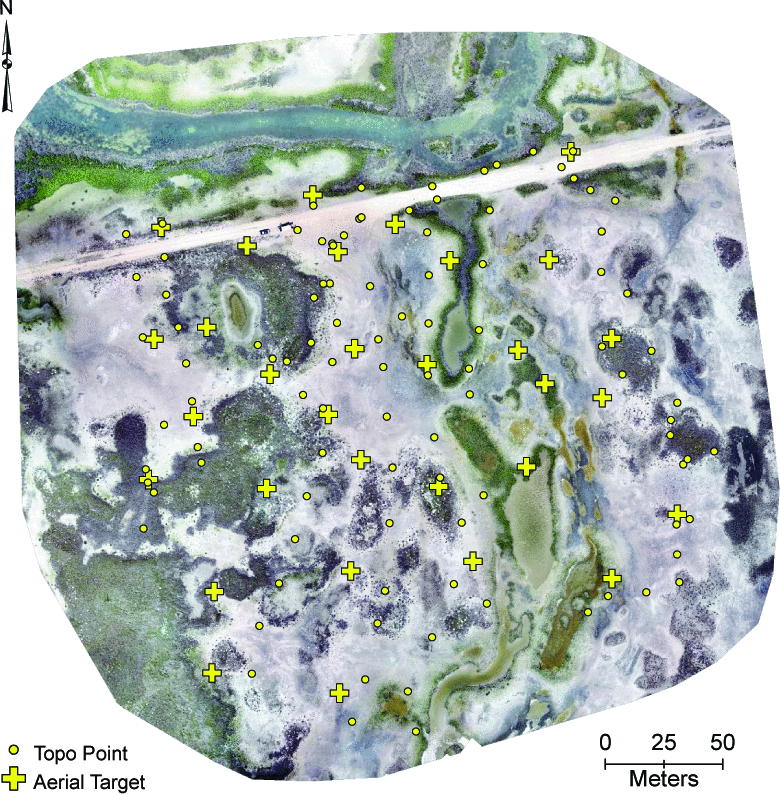
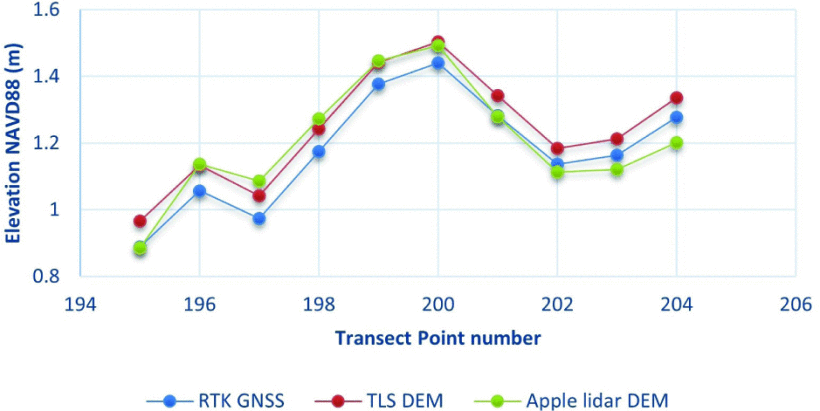
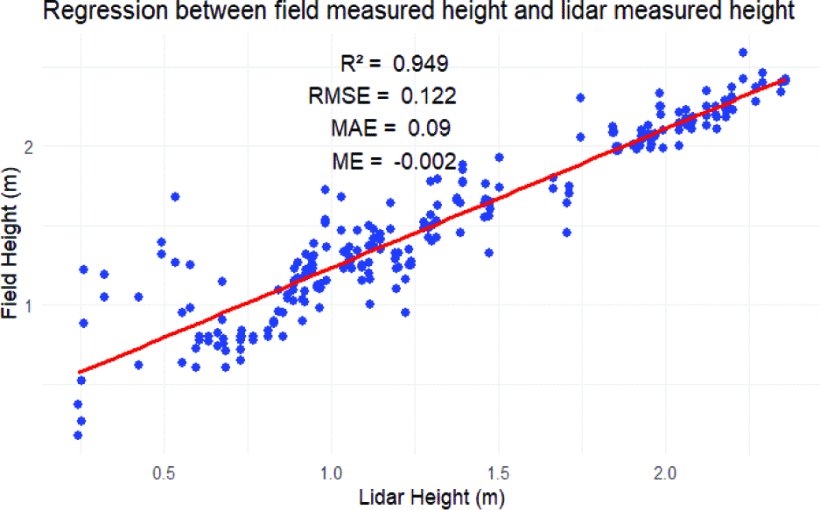
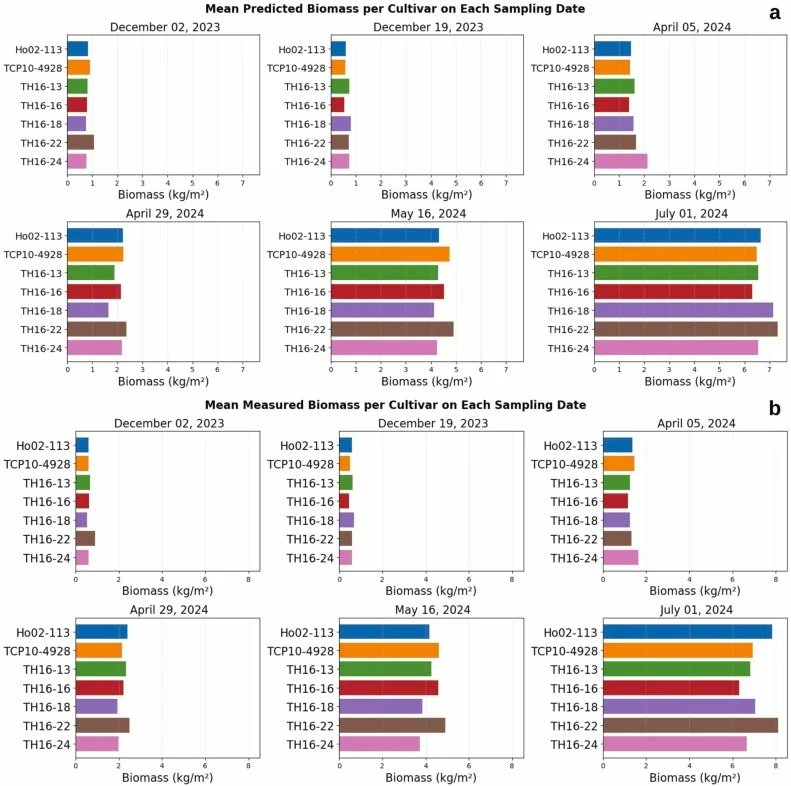
MANTIS Assistant Director Dr. Tianxing Chu and students Mohammad Sohail and Ahmed Omar attended the Geological Society of America (GSA) Annual Meeting held in San Antonio, Texas, from October 19-22, 2025. The event brought together geoscientists and researchers from around the world to share advancements in Earth science and geospatial technologies.
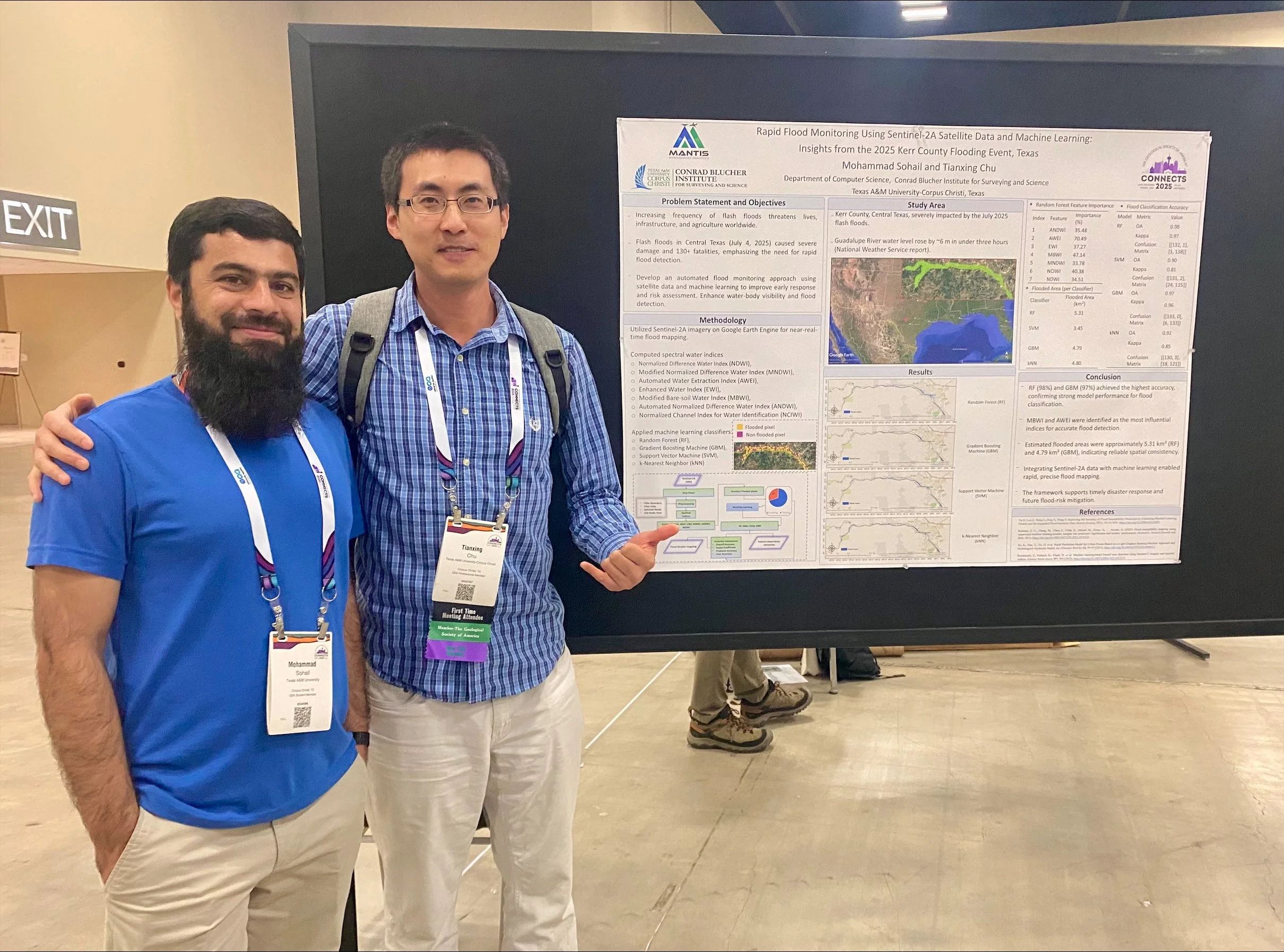
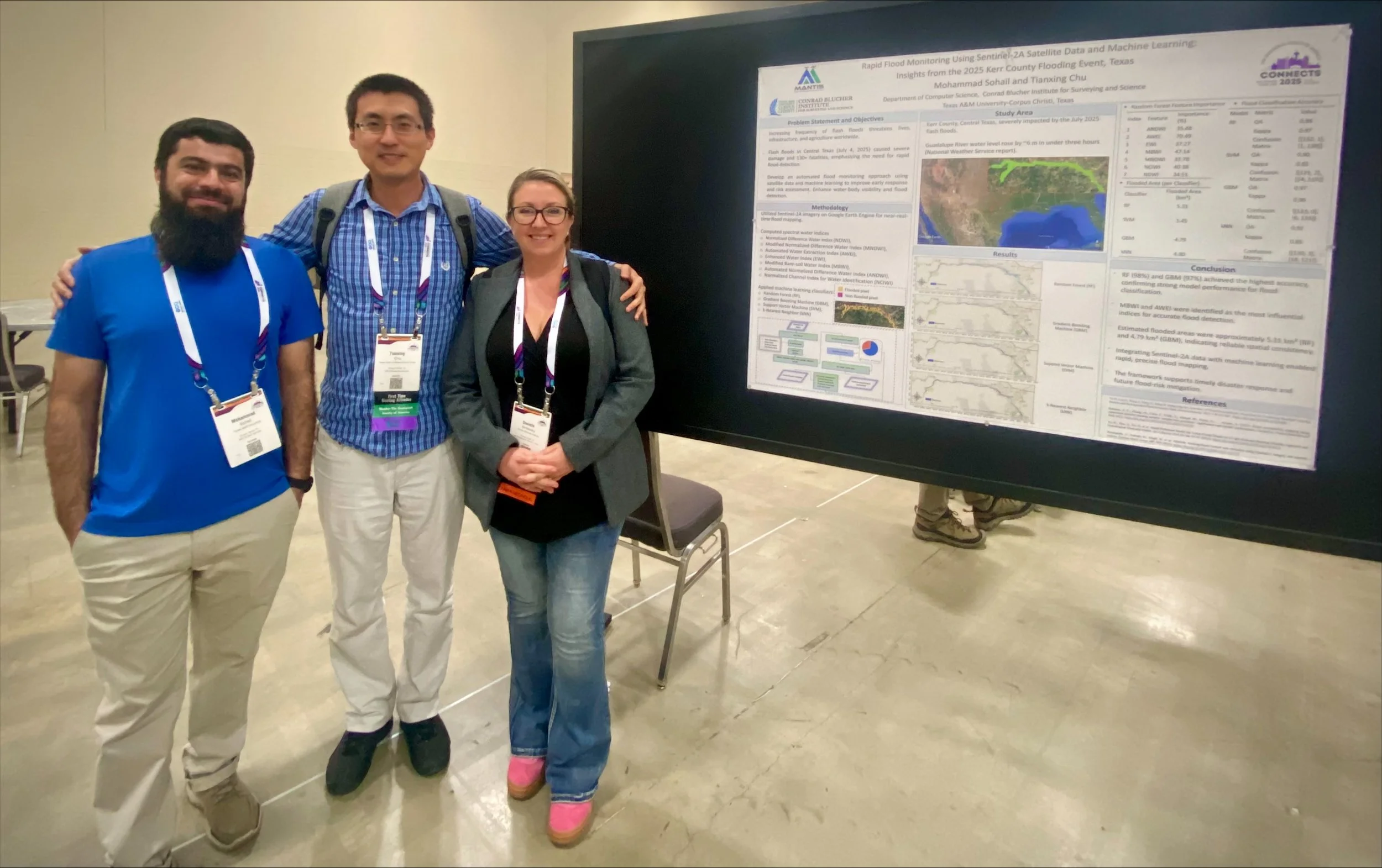
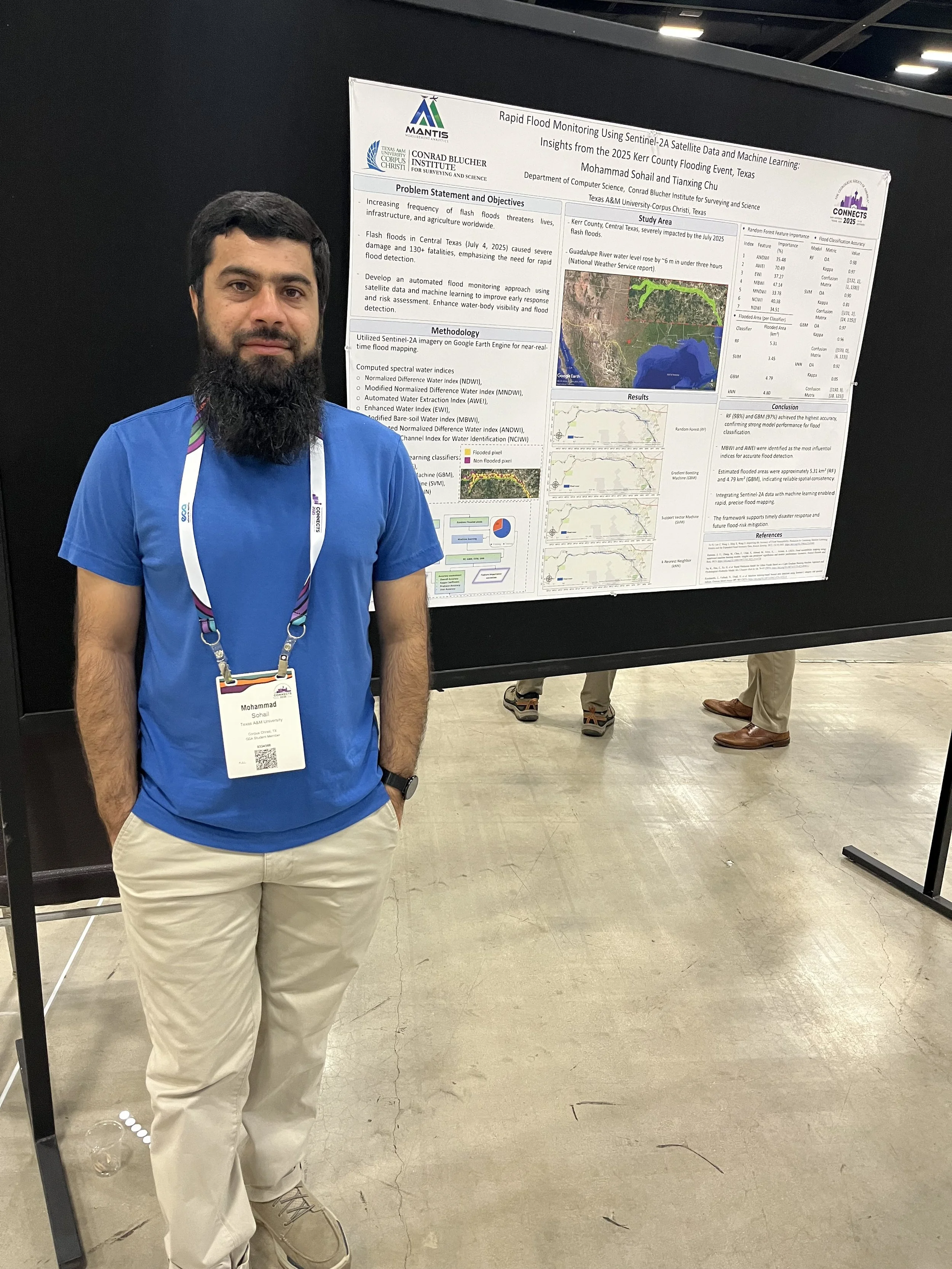
Mohammad Sohail, MANTIS Ph.D. student in Computer Science, presented his research titled “Rapid Flood Monitoring Using Sentinel-2A Satellite Data and Machine Learning: Insights from the 2025 Kerr County Flooding Event, Texas.” His study focused on the devastating flash floods that struck Central Texas, where the Guadalupe River rose by nearly six meters within hours. Mohammad developed an automated flood-mapping framework using Sentinel-2A imagery, spectral water indices, and machine learning algorithms on the Google Earth Engine platform. His approach highlights how satellite-based analytics can support rapid disaster response and flood-risk assessment. In addition, Mohammad volunteered as a Field Guide and Map Attendant, assisting conference participants and contributing to the event’s organization.
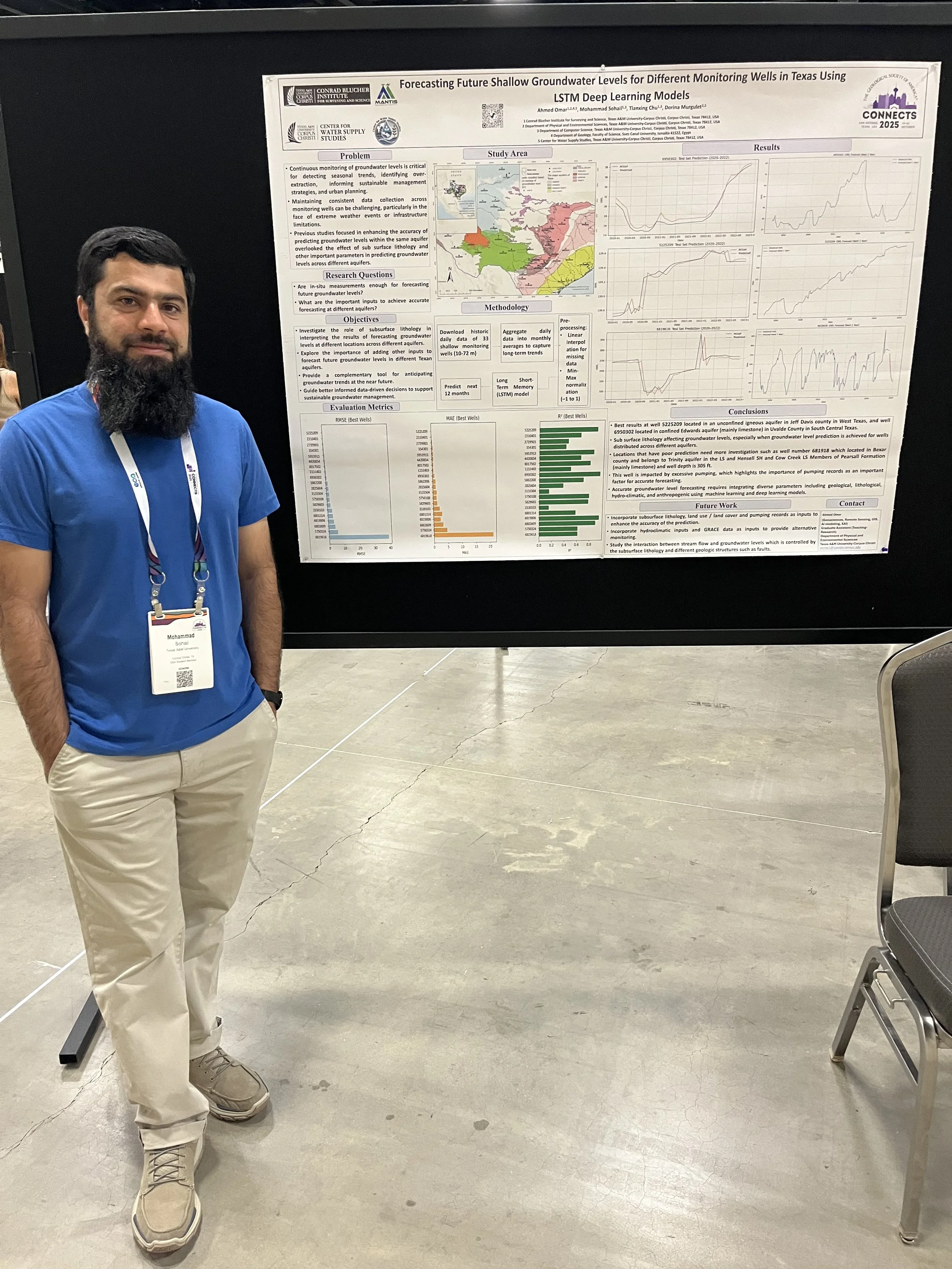
Ahmed Omar, also a MANTIS Ph.D. student in Coastal Marine Systems Science, delivered both a poster and an oral presentation showcasing his work on groundwater modeling and AI. His poster presentation, titled “Forecasting Future Shallow Groundwater Levels for Different Monitoring Wells in Texas Using LSTM Deep Learning Models,” demonstrated the capability of Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) deep learning models to forecast groundwater levels up to one year in advance using only historical groundwater data. The study highlighted the value of LSTM models as a complementary tool to traditional monitoring networks, particularly in areas with intermittent data availability or limited resources. In addition, his oral presentation, titled “Data-Driven Long-Term Monitoring of Groundwater Levels in Shallow, Intermediate, and Deep Wells Across Different Regions of Texas by Utilizing Remote Sensing Data, GIS, and Various AI Techniques,” introduced a framework that integrates remote sensing, meteorological, geologic, and GIS-derived variables with advanced machine learning and xAI methods. The inclusion of static geologic features and well classification by groundwater elevation enhanced model accuracy and interpretability across well groups. Using Shapley Additive exPlanation (SHAP) values, Ahmed provided insights into the relative importance of predictors at global and local scales, improving model transparency and reliability. This framework advances the methodological frontier of groundwater modeling in data-sparse regions and offers a scalable, transferable solution for sustainable groundwater management under changing climatic and land use conditions.
Dr. Danielle Smilovsky, a CBI member who collaborates closely with Dr. Chu, led a presentation titled “Recharged but not Recovered: InSAR Observations of Persistent Land Subsidence in Arizona’s Willcox Basin.” Her work used satellite interferometry to analyze ongoing land deformation despite groundwater recharge efforts.
Dr. Chu provided supervision and guidance to the students, underscoring MANTIS’s commitment to mentorship, innovation, and collaborative research in geospatial analytics.
The GSA 2025 conference offered valuable exposure, networking opportunities, and professional development for MANTIS members, further strengthening the lab’s contributions to applied geoscience research.